Our Legacy
No person will make a great business who wants to do it all himself or get all the credit.
– Andrew Carnegie
The Early Years
The Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching was established in 1905 and chartered in 1906 by an act of Congress as an independent policy and research center called to “do and perform all things necessary to encourage, uphold, and dignify the profession of the teacher and the cause of higher education.” Today the mission of the Foundation is to catalyze transformational change in education so that every student has the opportunity to live a healthy, dignified, and fulfilling life.
Andrew Carnegie—an American industrialist and a leading philanthropist of his time—created the Foundation to address what he perceived as a pressing issue on the education landscape at the time: the lack of any form of retirement plan or system for the faculty at institutions of higher education. His concern first surfaced as a trustee of Cornell University and through conversations with his friend Henry Pritchett, President of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, that made evident the low salaries of higher education faculty and the glaring poverty into which most professors retired. As a result, Carnegie established the Foundation as a general pension fund for a wide range of universities in the United States, Canada, and Newfoundland.
To move forward with its mission, the Foundation found that it needed to determine which schools qualified as a bona fide institution of higher education and which of their faculty qualified for pensions. The resulting eligibility standards created by the Foundation became the most widely used basis for the admissions requirements and instructional policies of colleges and universities, as well as the graduation requirements for high schools. Higher education institutions soon adopted what came to be known as the “Carnegie Unit” to measure students’ progress through a course of study in terms of Carnegie credit hours—a measure in which one hour per week of contact between student and faculty equaled one credit. This early impact of these standards on educational organization and practice in secondary and postsecondary education in the United States continues to this day.
In 1918, the Foundation spun off the pension fund as an independent not-for-profit organization known as TIAA-CREF (now known as TIAA) that serves as the world’s largest retirement management system for academics, researchers, and individuals in the public serving not-for-profit sector. TIAA has served as a model for numerous other employee retirement benefit systems, and many of its structural elements and procedures were influential on the first federal oversight of such plans, the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 and its attendant regulations.

Significant Contributions
Throughout its more than 115-year history, the Carnegie Foundation has made a number of contributions to the field of education generally and higher education in particular. The most significant of these are briefly summarized here.
Education in the Professions
Medicine
Henry Pritchett, first President of the Foundation, commissioned several studies that revolutionized the field of medical education. First among these, in 1910, was Abraham Flexner’s Medical Education in the United States and Canada—more commonly known as the Flexner Report—which exposed wide variation in admissions requirements, curricula, facilities, assessment methods, and graduation requirements across the 155 medical schools in operation at the time. Flexner recommended that physician training be standardized and composed of education in biomedical sciences paired with clinical practice in academic hospitals. The report ignited protests and debate across the country, but it ultimately resulted in higher standards for medical schools and a complete transformation of the structure of medical education to that which exists today.
Engineering
The release of the Flexner Report created an interest in studies of professional education in other fields. In 1918, the Foundation commissioned and published A Study of Engineering Education, which argued for a revised common curriculum that emphasized science and the practice of applying the principles undergirding engineering in the field, adequate training for teachers of engineering, and the creation of objective admissions tests. The report led to the founding of the Engineer’s Council for Professional Development in 1932 (renamed the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology in 1980). Today, technical professionals from ABET’s member societies develop the criteria used in accrediting university engineering programs.
Teaching
In 1915, the Governor of Missouri and the state’s Department of Education invited the Foundation to study the conditions of the state’s “normal schools”—that is, teacher-training colleges. Released in 1920, The Professional Preparation of Teachers for American Public Schools: A Study Based Upon an Examination of Tax-Supported Normal Schools in the State of Missouri, known as the Missouri Study, examined the process of teacher preparation and recommended that normal schools focus on the professional preparation of educators rather than on other academic work. This report led to the first steps toward the professionalization of teaching, the transition of normal schools to teacher colleges by the 1930s, and the eventual incorporation of teacher colleges into schools of education within universities.
Dentistry
In the 1920s, the Foundation commissioned William Gies, a biochemistry professor at Columbia University to conduct the first study of dental education. The resulting report, Dental Education in the United States and Canada, The report revealed the critically low standards in most dental schools. From this report came recommendations that each incoming dental student have a minimum of two years of postsecondary education, that biomedical science be included in the dental curriculum, and that dental schools receive support from universities along the same lines as the support given to medical schools based upon the Flexner Report. The Gies Report spurred the implementation of higher requirements for admission and accreditation and established dentistry’s place as an essential component of higher education in the health professions.
Law
In 1914, at the invitation of the American Bar Association, the Foundation conducted a study leading to the publication of its influential report, The Common Law and the Case Method in American University Law Schools. It recognized the significant strengths of the case method, while also cautioning against an overdependence upon it, which would not sufficiently prepare students to see the law as a dynamic entity and understand its role at the intersection of history and ethics. The case method is the foundation of most law school classes today.
Higher Education Assessment
In 1937, under the leadership of then President Walter Jessup, the Foundation extended its work in professional education by developing and administering the Graduate Record Examination (GRE) to assist universities in their graduate school admissions processes. The Foundation continued to administer the exam until 1947, when it collaborated with the College Entrance Examination Board and the American Council on Education to create the Educational Testing Service, which continues to administer the GRE (along with numerous other admissions-related examinations).
Higher Education Financial Support
The Carnegie Foundation founded the Carnegie Commission on Higher Education in 1968 and the Carnegie Council on Policy Studies in Higher Education in 1973. Led by Clark Kerr, former President of the University of California, these bodies together published more than 120 significant reports and studies on higher education in the United States. Eleven of these reports specifically addressed equality of opportunity in higher education, beginning with the influential Quality and Equality: New Levels of Federal Responsibility for Higher Education, which advocated for and contributed to the creation of policies that increased access to higher education. One of these is the Federal Pell Grant Program, which remains the largest source of federal grant aid to low-income students for undergraduate education. Another example is the Fund for the Improvement of Postsecondary Education, which was established to improve secondary educational opportunities and still continues to fund the development and dissemination of strategies for supporting all students, particularly those at risk of not completing their programs of study.
Carnegie Classifications
Basic Classification
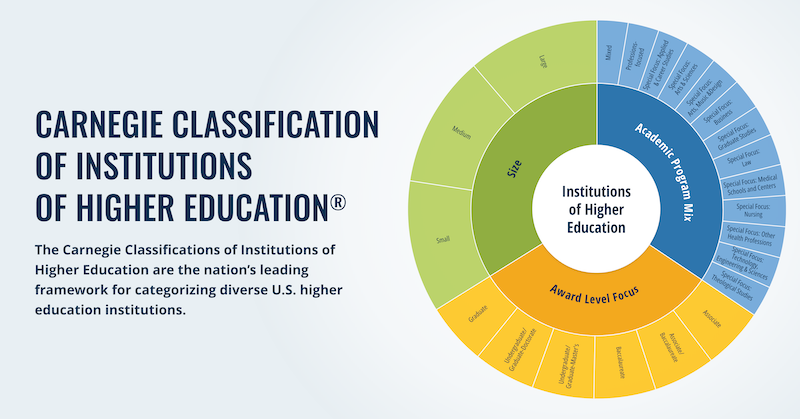
In 1971, under the leadership of Clark Kerr, the Carnegie Commission on Higher Education developed a classification system for describing colleges and universities. Initially intended to support research and policy analysis, the Carnegie Classification uses publicly available empirical data about characteristics of students and faculty as well as the work of the institutions to identify categories of like institutions based on function and mission, including doctoral-granting institutions, comprehensive universities and colleges, liberal arts colleges, two-year colleges and institutions, professional schools, and other specialized institutions. The classification system, periodically updated, functions as the most prominent and widely used framework guiding the study of higher education by describing and controlling for institutional diversity. The system itself has grown to include classifications of instructional program, enrollment profile, size and setting, and certain “elective” classifications.
Elective Classifications: Community Engagement and Leadership for Public Purpose
The Carnegie Elective Classifications of Institutions of Higher Education are entered into by colleges and universities on a voluntary basis. When conferred they represent an independent and rigorous warranting of the institution’s extraordinary commitment to, investment in, and accomplishment at some topical focus of that institution’s address of its public purpose in pursuit of common social good. Currently there are two elective classifications: Community Engagement and Leadership for Public Purpose.
In 2022, administrative and operational responsibility for all elements of Carnegie Classifications (Universal and Elective) was transferred to the American Council on Education (ACE). This allowed the Foundation to established a long term relationship to ensure stability of leadership as well as conceptual coherence and operational consistency to make the classifications more timely, relevant, and effective in serving the field of higher education.
Scholarship of Teaching
After the publication of two reports on the experience of students within the education system (High School: A Report on Secondary Education in America in 1983 and College: The Undergraduate Experience in 1986), President Ernest Boyer turned his attention to related scholarship. In Scholarship Reconsidered: Priorities of the (1990), he called for a reformation of academic scholarship by challenging the traditional roles of faculty as scholars. He argued that this role created an incongruity between the increased pressure on faculty to produce publishable work and the mission of colleges and universities to promote the intellectual and moral development of an increasingly diverse populace. His writing persuaded many colleges and universities to reexamine and revise the standards by which they judged faculty work. This work was followed by the 1997 publication of Scholarship Assessed: A Special Report on Faculty Evaluation, in which authors Charles Glassick, Mary Taylor Huber, and Gene I. Maeroff described the changing nature of scholarship in institutions of higher education.
Under President Lee Shulman’s leadership, the Foundation expanded on work done in its first 100 years by becoming a center for the advanced study of teaching at all levels and across many disciplines. As part of this renewed focus on the scholarship of teaching, the Foundation launched the Carnegie Academy for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning (CASTL) in 1998, which included programs for campuses and disciplinary associations, national fellowship programs for teachers in K–12, and collegial associations in which college and university faculty in diverse fields came together to develop a scholarship of teaching and learning. A collection of Shulman’s writing, The Wisdom of Practice: Essays on Teaching, Learning and Learning to Teach, received the University of Louisville’s Grawemeyer Award in Education in 2006.
At the same time, the Foundation launched the Preparation for the Professions Program—a multiyear study of professional education that would compare approaches to teaching and learning across professions. Reminiscent of the early-20th-century reports following the Flexner Report, these new studies examined the preparation of physicians, engineers, lawyers, teachers, nurses, and the clergy.
The Foundation also turned its attention to studies on doctoral education, working with leadership teams from over 80 departments in six fields (chemistry, education, English, history, mathematics, and neuroscience). The Carnegie Project on the Education Doctorate (CPED) engaged more than 50 schools of education in a critical evaluation and redesign of the Ed.D. to increase the degree’s relevance for faculty and leaders in school systems. Today, the University of Pittsburgh houses CPED, which is made up of 105 institutions in the United States, Canada, and New Zealand.
Advancing Teaching–Improving Learning
The Advancing Teaching–Improving Learning program sought to enhance the capacity of those working in the field of teacher assessment and evaluation by helping them to learn from emerging practices to build more effective information systems to advance teacher quality.
Knowledge Media Lab
The Knowledge Media Laboratory worked to create a future in which communities of teachers, faculty, programs, and institutions collectively advanced teaching and learning by exchanging their educational knowledge, experiences, ideas, and reflections by taking advantage of various technologies and resources.
Undergraduate Education
Carnegie’s undergraduate education programs from 1997 to 2009 investigated the conditions under which teaching and learning took place and what they looked like. The focus was on ways to improve and advance classroom teaching and learning at colleges and universities. This work also supported a view of liberal education that included a commitment to diversity and to the empowerment of students as participating and contributing members of society. These programs include:
- The BELL Project
- Cultures of Teaching and Learning
- Integrative Learning Project
- Higher Education and the Development of Moral and Civic Responsibility
- Political Engagement Project
- Strengthening Pre-Collegiate Education in Community Colleges (SPECC)
U.S. Professors of the Year
From 1981 to 2015, the Professors of the Year program honored outstanding faculty members for their achievement as undergraduate professors. Sponsored by the Council for Advancement and Support of Education and the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching, it was the only national program to recognize excellence in undergraduate teaching and mentoring.